Montessori Learning Through Sensorial Work
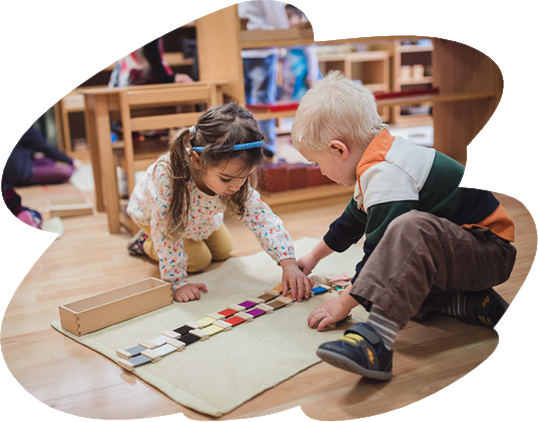 The concept of sensorial work was developed by Dr Montessori long before sensory play was adopted into practice.
The concept of sensorial work was developed by Dr Montessori long before sensory play was adopted into practice.
According to the Montessori philosophy, the child is the “sensorial explorer” and learns to perceive qualities through sensorial experiences.
Dr Maria Montessori believed that sensorial experiences began at birth. Through their senses, children are able to study their environment.
Through sensorial work, children are able to consciously obtain clear information that allows them to make classifications in their environment.
These classifications also work as stepping stones to organised intelligence, which leads to the ability to adapt to the environment.
“The senses, being explorers of the world, open the way to knowledge. Our apparatus for educating the senses offers the child a key to guide his explorations of the world; they cast a light upon it which makes visible to him more things in greater detail than he could see in the dark, or uneducated state.” Maria Montessori: The Absorbent Mind, chapter 17, p 167.
However, the sensory perception of an adult is different than the sensory perception of a child. In their purest of forms, children have special sensitivity to absorb information through their senses, categorise it and create mental order and orientation of the things in their environment.
The Sensorial materials offer particular assistance to these aspects of the child’s self-construction. They also offer opportunities for development as motivated by the Human Tendencies for Exploration, Order, Abstraction, and Exactness throughout the period 3-6, thereby preparing the Constructive Powers.
We provide the main activities
The Five Senses and the Qualities They Perceive
The Activities of the Sensorial Area are organised according to the information (Perceptions) gathered by the five sensory organs of the body:
contact us
Curriculum
Elements
Touch
Skin, specifically the Hand e.g Touch Board; Touch the Fabric
Sight
Eyes e.g Pink Tower; the Color Tablets
Hearing
Ears e.g Sound Boxes; Bells
Smell
Nose e.g smelling bottles distinguish, identify and name different smells
Taste
Tongue e.g salt, sweet, bitter, and sour